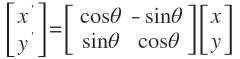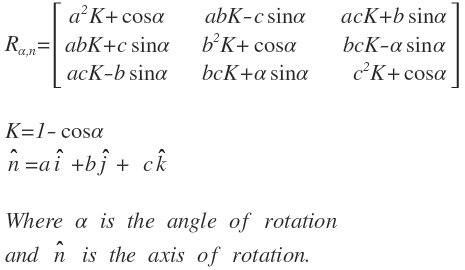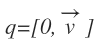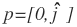Introduction
Rotations in computer graphics is a transformational operation. That means that it is a conversion from one coordinate space onto another. Rotational transformation can be accomplish with Matrices or with Quaternions. You will learn how a vector can be rotated with both methods. Although Quaternions offer a better solution than matrices, it is a good idea to learn how matrices rotate a character in 3D games.
Rotation with Matrices
2D Rotations
The matrix for rotating a point about an origin in a 2D plane is defined as:
Thus the rotation of a 2D vector in a plane is done as follows:
For example: To rotate a vector 90 degrees counterclock-wise is done as follows:
3D Rotations
Rotation about z-axis
We can generalized the above matrix to work in a 3D world by adding a third coordinate. For example, to rotate about the z-axis, we can add a z-coordinate as shown below:
For example, to rotate a vector about the z-axis 90-degrees counterclock-wise is done as follows:
Rotation about x-axis
If you would like to rotate a point about the x-axis, the x-coordinate is kept constant while the y-and z-coordinate are changed as shown below:
For example, to rotate a vector about the x-axis 90 degrees counterclock-wise is done as follows:
Rotation about y-axis
In the same manner, to rotate about the y-axis, the y-coordinate remains constant, while the x- and z-coordinates are changed as shown below.
For example, to rotate a vector about the y-axis 90 degrees counterclock-wise is done as follows:
Composite rotation with matrices
The rotation transforms can be combined into forming one concatenated rotation transform. For example, the rotation transform below will rotate a vector in the following manner:
- First Rotate about z-axis
- Then Rotate about y-axis
- Finally, Rotate about x-axis
When working with concatenated matrices, the order of rotation matters. In the above example, the right-most transform occurs first and the left-most transform occurs last. Always remember that concatenated matrices are performed from right to left. Also note the following property:
The result depends on matrix order!
Rotation about an arbitrary axis
Rotations about an arbitrary axis is possible with matrices. The matrix below shows the mathematical representation of such transform:
Rotation with Quaternions
In order to understand how Quaternions rotate a vector, you need to understand the concept of a Pure Quaternion and a Unit-Norm Quaternion. A pure quaternion is simply a quaternion with a scalar of zero. A pure quaternion only contains a vector component. The vertices of a character can be considered as pure quaternions while rotating the character. Mathematically, a pure quaternion is represented as:
A quaternion is also defined as:
However, when a quaternion is defined as follows:
A vector is rotated about the axis v by an angle theta. For this rotation to occur, the vector; represented as a pure quaternion, is multiplied by the quaternion and its inverse. This quaternion representation is represented as follows:
For example, to rotate a vector (0,1,0) by 90 degrees about the x-axis is done as follows:
The inverse of q is:
and the pure quaternion is simply the vector (0,1,0).
Thus, to rotate the vector (0,1,0) about the x-axis:
Keep in mind that q must normalized.
If you would like to know more about quaternions, I strongly advise you to take a look at this book: Quaternions for Computer Graphics by John Vince